感想
引用在网上搜索的资料:
装饰者模式:动态的将新功能附加到对象上。在对象功能扩展方面,它比继承更有弹性 。
意图: 动态地给一个对象添加一些额外的职责。就增加功能来说, Decorator模式相比生成子类更为灵活。该模式以对客 户端透明的方式扩展对象的功能。
适用环境:
(1)在不影响其他对象的情况下,以动态、透明的方式给单个对象添加职责。
(2)处理那些可以撤消的职责。
(3)当不能采用生成子类的方法进行扩充时。一种情况是,可能有大量独立的扩展,为支持每一种组合将产生大量的 子类,使得子类数目呈爆炸性增长。另一种情况可能是因为类定义被隐藏,或类定义不能用于生成子类。
参与者:
1.Component(被装饰对象的基类):定义一个对象接口,可以给这些对象动态地添加职责。
2.ConcreteComponent(具体被装饰对象):定义一个对象,可以给这个对象添加一些职责。
3.Decorator(装饰者抽象类):维持一个指向Component实例的引用,并定义一个与Component接口一致的接口。
4.ConcreteDecorator(具体装饰者):具体的装饰对象,给内部持有的具体被装饰对象,增加具体的职责。
1.模式结构
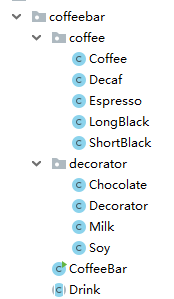
2.关键在于Coffee,Decorator,Drink,代码如下:
Coffee:1
2
3
4
5
6
7public class Coffee extends Drink {
public float cost() {
return super.getPrice();
}
}
Decaf:1
2
3
4
5
6
7public class Decaf extends Coffee {
public Decaf() {
super.setDescription("Decaf");
super.setPrice(3.0f);
}
}
Espresso:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8public class Espresso extends Coffee {
public Espresso() {
super.setDescription("Espresso");
super.setPrice(4.0f);
}
}
LongBlack:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8public class LongBlack extends Coffee {
public LongBlack() {
super.setDescription("LongBlack");
super.setPrice(6.0f);
}
}
ShortBlack:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8public class ShortBlack extends Coffee {
public ShortBlack() {
super.setDescription("ShortBlack");
super.setPrice(5.0f);
}
}
Chocolate:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9public class Chocolate extends Decorator {
public Chocolate(Drink Obj) {
super(Obj);
super.setDescription("Chocolate");
super.setPrice(3.0f);
}
}
Decorator:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19public class Decorator extends Drink {
private Drink Obj;
public Decorator(Drink Obj) {
this.Obj = Obj;
}
public float cost() {
return super.getPrice() + Obj.cost();
}
public String getDescription() {
return super.description + "-" + super.getPrice() + "&&" + Obj.getDescription();
}
}
Milk:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9public class Milk extends Decorator {
public Milk(Drink Obj) {
super(Obj);
super.setDescription("Milk");
super.setPrice(2.0f);
}
}
Soy:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9public class Soy extends Decorator {
public Soy(Drink Obj) {
super(Obj);
super.setDescription("Soy");
super.setPrice(1.5f);
}
}
CoffeeBar:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18public class CoffeeBar {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Drink order;
order = new Decaf();
System.out.println("order1 price:" + order.cost());
System.out.println("order1 desc:" + order.getDescription());
System.out.println("****************");
order = new LongBlack();
order = new Milk(order);
order = new Chocolate(order);
order = new Chocolate(order);
System.out.println("order2 price:" + order.cost());
System.out.println("order2 desc:" + order.getDescription());
}
}
Drink:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24public abstract class Drink {
public String description = "";
private float price = 0f;
public void setDescription(String description) {
this.description = description;
}
public String getDescription() {
return description + "-" + this.getPrice();
}
public float getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(float price) {
this.price = price;
}
public abstract float cost();
}

